Long-Term Care Insurance
Is LongTerm Care benefits part of your income plan?
Aging isn’t the only reason to plan for long-term care — it is also there for clients if a chronic illness or
disabling injury prevents them from living on their own or properly caring for themselves, no matter
how old they are. Long-term care refers to services that are provided to someone who has a chronic
condition that’s progressive in nature, gets worse as time goes on, and generally has no cure.
Long-term
care helps with day-to-day tasks like bathing, eating, getting dressed, and getting in and out of bed.
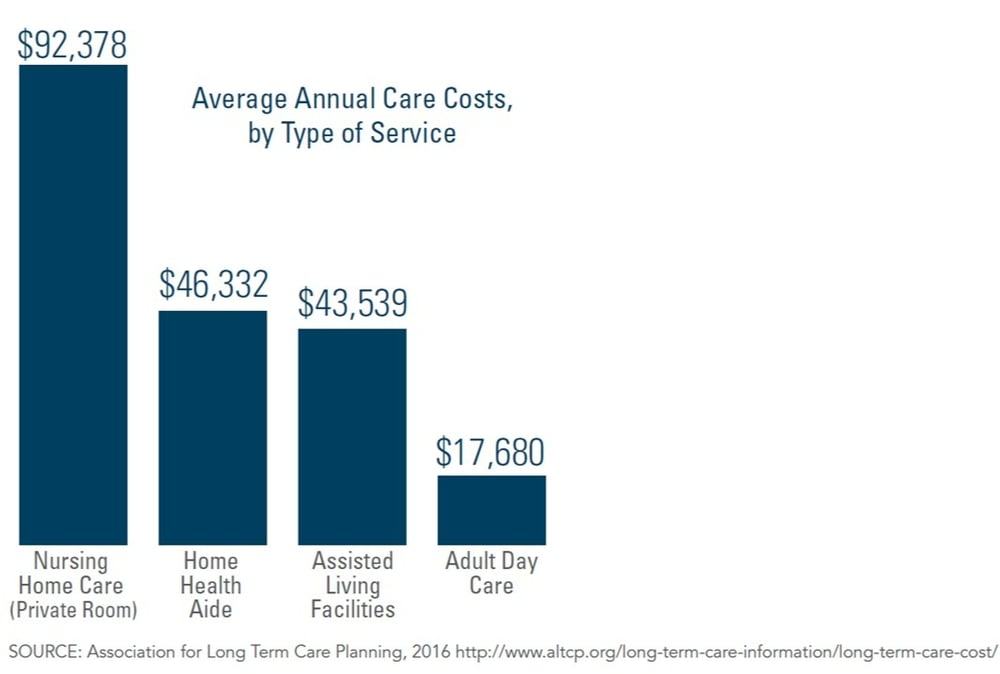
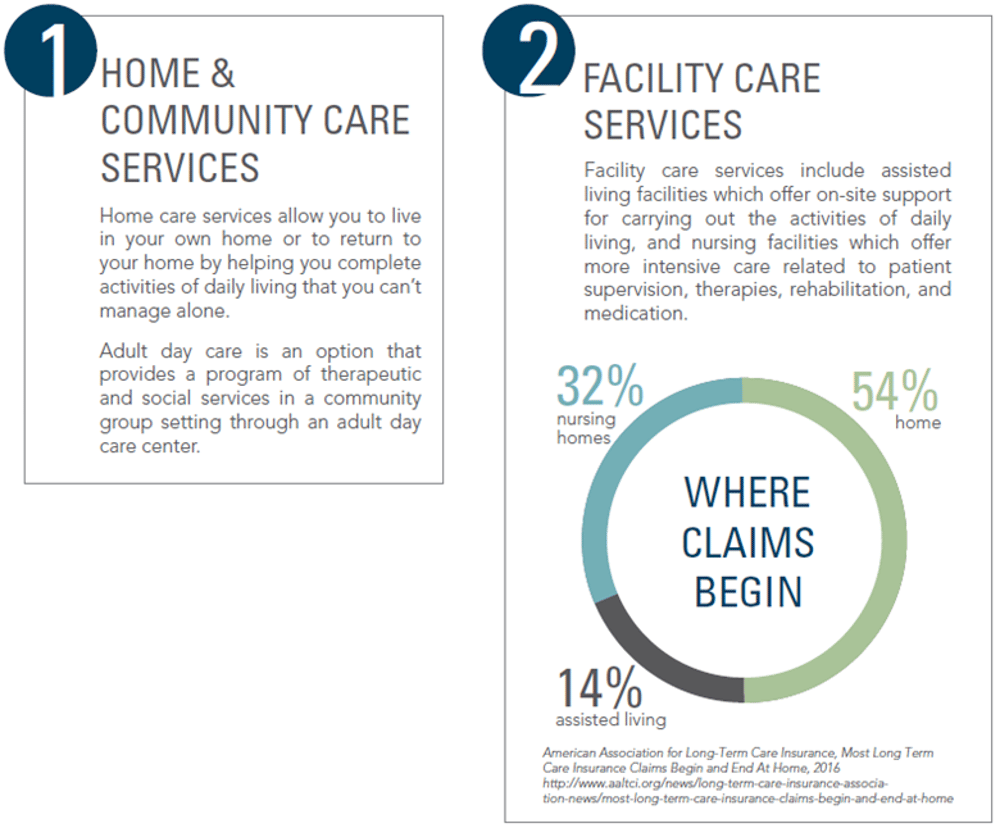
Long-term care insurance is designed to reimburse some of the costs of receiving various levels of care
for chronically ill individuals, either in their home, in the community, at an assisted living facility, or in a
nursing home
Schedule your long-term care review.
Glossary of Long-Term Care
Activities of Daily Living (ADLs) — Everyday functions and activities individuals usually do without help. ADL functions
include bathing, continence, dressing, eating, toileting and transferring.
Assisted Living Facility — A residential living arrangement for people who may need assistance with one or more activities of daily living, but do not require the level of care provided in a nursing home. They can range from a
small home to a large apartment-style complex. Services include laundry, meals, socialization and transportation in addition to personal care, medication management and memory care supervision and support.
Cancer — Also called malignancy, is characterized by an abnormal growth of cells. There are more than 100 types of
cancer, including breast cancer, skin cancer, lung cancer, colon cancer, prostate cancer, and lymphoma. Cancer symptoms
vary widely based on the type.
Cardiovascular Disease — Disease affecting the heart or blood vessels. Some conditions that fall under the umbrella of
cardiovascular disease are aneurysm, angina, arrhythmia, cardiomyopathy, congenital cardiovascular defects, congenital
heart disease, congestive heart failure, heart attack, diseases of pulmonary circulation, endocarditis, rheumatic fever,
stroke, heart valve disease, diseases of the circulatory system.
Chronic Illness— A chronically ill individual is a person who has been certified by a licensed health care practitioner as
being unable to perform, without assistance, at least two activities of daily living (ADLs) for at least 90 days, or has been
certified to have cognitive impairment.
Cognitive Impairment— Requires substantial supervision due to a deficiency in a person’s short- or long-term memory;
orientation as to person, place and time; deductive or abstract reasoning; or judgment as it relates to safety awareness.
High Blood Pressure — (Hypertension) Blood pressure readings are measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and
usually given as two numbers — for example, 120 over 80 (written as 120/80 mmHg). One or both of these numbers can
be too high. The top number is your systolic pressure. It is considered high if it is over 140 most of the time. It is
considered normal if it is below 120 most of the time. The bottom number is your diastolic pressure. It is considered high if
it is over 90 most of the time. It is considered normal if it is below 80 most of the time.
High Cholesterol — is the presence of high levels of cholesterol in the blood. It is not a disease but a metabolic
derangement that can be secondary to many diseases and can contribute to many forms of disease, most notably
cardiovascular disease. Primarily caused by diet and family history high cholesterol is defined as a measurement greater
than 200 mg/dL. LDL cholesterol levels greater than 130 mg/dL and HDL cholesterol levels less than 60 mg/dL are
considered high.
Home Health Aide – A trained and certified health care worker who provides personal care services such as bathing and dressing in addition to light household duties like meal preparation.
Home Health Care — Services for nursing care or occupational, physical, respiratory or speech therapy. Also included are medical, social worker, home health aide, and homemaker services
Licensed Practical Nurse (LPN) – A nurse who practices under the direction of a physician and cares for people who are sick, injured, in rehabilitation or disabled. Typically, an LPN has completed two years of specialized training and has passed a licensing exam.
Life Expectancy — The age which is calculated either actuarially, or manually, to estimate medical costs to.
Medicare — A federal system of health insurance for people over 65 years of age and for certain younger people with
disabilities.
Medicare Part A — Hospital insurance that helps cover inpatient care in hospitals, skilled nursing facility, hospice, and
home health care.
Medicare Part B — Helps cover medically necessary services like doctors’ services, outpatient care, home health
services, and other medical services.
Medicare Part D — Prescription drug coverage that is purchased through private insurance companies.
Medicare Premium — The amount of money a person pays to cover Medicare B, D, and Supplemental (MediGap).
Medicare Supplemental Insurance (MediGap) — Medicare Supplemental Insurance policies fill in the gaps that
Medicare Parts A & B do not cover. This report assumes premiums for MediGap Plan G and uses the average cost for this
plan in the subscriber’s state of residence.
Multiple Sclerosis — Multiple sclerosis is a nerve disorder that occurs when the insulating layer surrounding neurons in
the brain and spinal cord are destroyed. The disease is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects the movements,
sensations, as well as body functions.
Myelin — a part of the brain, helps in passing electrical signals between the brain and
the other parts of the body. When this part is destroyed the brain functioning is less efficient.
Nursing Home – A licensed facility that provides 24-hour room and board, plus general nursing care and personal care assistance to those who are chronically ill or unable to take care of daily living needs, or who need supervision and support due to a cognitive impairment. May also be referred to as a Long-Term Care Facility.
Premium — The amount of money needed to pay for insurance coverage. Before age 65 this would reflect a payment to
a COBRA policy or an Insurance company. After age 65 the Medicare premiums would be reflected.
Registered Nurse (RN) – A specially-trained nurse who coordinates and provides patient care. RNs hold either a bachelor’s degree in nursing, an associate’s degree in nursing or a diploma from an approved nursing program and are licensed to practice by the state.
Retirement Age — The age at which each person plans to retire.
Skilled Care — Daily nursing and rehabilitative care that can be performed only by, or under the supervision of, skilled
medical personnel. This care is usually needed 24 hours a day, must be ordered by a physician, and must follow a plan of
care. Individuals usually get skilled care in a nursing home but may also receive it in other places.
Type 1 Diabetes — aka juvenile diabetes, or insulin-dependent diabetes, which is a chronic condition in which the pancreas
produces little or no insulin, a hormone needed to allow sugar (glucose) to enter cells to produce energy. Various factors
may contribute to type 1 diabetes, including genetics and exposure to certain viruses. Although type 1 diabetes typically
appears during adolescence, it can develop at any age.
Type 2 Diabetes — (formerly called non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM), or adult-onset diabetes) is a
disorder that is characterized by high blood glucose in the context of insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency.
